Understanding VPS: How it Works, Benefits, and Common Uses
1. What is VPS?
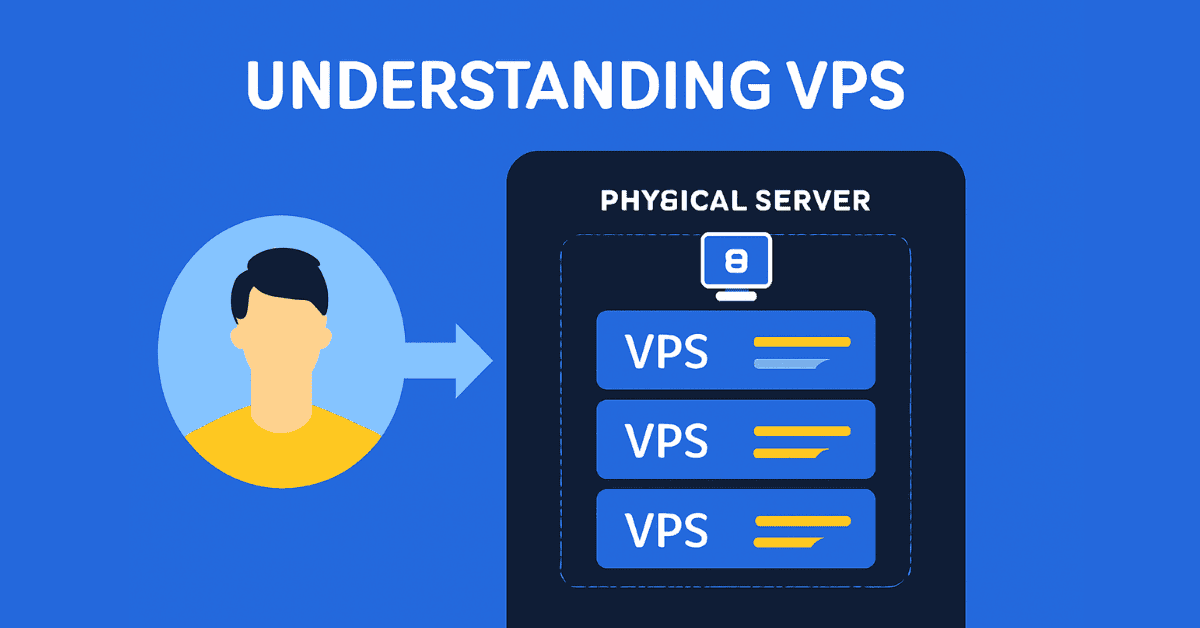
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a virtual machine created by partitioning a physical server into multiple independent virtual servers. Each VPS operates like a standalone server with its own resources (CPU, RAM, hard disk space), but shares the physical hardware with other VPSs.
2. How Does VPS Work?
VPS operates using virtualization technology, dividing a physical server into separate, independent VPSs. Each VPS has its own operating system and software, and only registered users have full access to all resources and can configure the system.
3. Uses of VPS
3.1 Running a Website
VPS provides high performance and security, ensuring smooth website operation and handling large amounts of traffic. It allows the installation of web management software like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal.
3.2 Hosting Applications
VPS is ideal for hosting various web applications like e-commerce sites, forums, CRM apps, and even game servers. It offers a separate environment to run applications, improving performance and security.
3.3 Software Development
Software developers can use VPS to test and deploy applications. VPS allows root access, enabling the installation and configuration of software as needed.
3.4 Data Backup
VPS can also be used for safely backing up personal or business data, offering large storage space and excellent security.
4. VPS vs Web Hosting: The Difference
Both VPS and Web Hosting are web hosting services, but VPS provides more control over resources and software. While Web Hosting typically shares resources among users, VPS offers separate space and resources.
5. Pros and Cons of VPS
5.1 Pros
- Flexibility: Full system control with root access.
- High Performance: Ensures smooth operation even with high traffic.
- Security: Each VPS operates independently, providing better protection.
- Scalability: Easily upgrade storage and other resources.
5.2 Cons
- Technical Knowledge Required: Users need system administration skills.
- Higher Cost: VPS is generally more expensive than shared hosting.
- Troubleshooting Challenges: Users need to handle issues themselves or contact the service provider.
- Not Suitable for Low Traffic Sites: VPS may waste resources for websites with low traffic.
In conclusion, VPS is an excellent solution for large websites, high-performance applications, security needs, and blockchain services like node running.